 Arctic ocean
Arctic ocean
The
Atlantic Ocean is the world’s second largest ocean, behind the Pacific Ocean. With a total area of about 106,400,000 square kilometres (41,100,000 sq mi), it covers approximately 20 percent of the Earth’s surface and about 29 percent of its water surface area. The first part of its name refers to Atlas of Greek mythology, making the Atlantic the “Sea of Atlas”.
 Atlantic ocean
Atlantic ocean
The
Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world’s five major oceanic divisions.
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the
Arctic Mediterranean Sea or simply the
Arctic Sea, classifying it a mediterranean sea or an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. Alternatively, the Arctic Ocean can be seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.
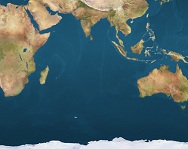 Indian ocean
Indian ocean
The
Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world’s oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth’s surface.
It is bounded by Asia—including India, after which the ocean is named
on the north, on the west by Africa, on the east by Australia, and on the south by the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, by Antarctica).
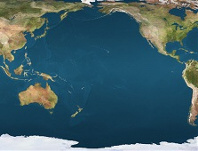 Pacific ocean
Pacific ocean
The
Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth’s oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.